electron geometry chart|VSEPR Theory & Chart : Manila Learn how to predict the shapes of molecules using Lewis electron dot structures and VSEPR theory. See the chart of electron-group geometry, molecular geometry, VSEPR notation and ideal bond angles for different numbers of electron groups and lone pairs. Tingnan ang higit pa Best sureball STL hearing today & 3d Lotto Swertres hearing today & Tomorrow 9PM, 5PM, 2PM Visayas and Mindanao. 3d lotto Guide Tips for Today. . Kuya Ely, Elma Mulawin, Rambolito, 3-D lotto, 3D Shooter guide, Megatip, Mastertip, Bolantoy, Batenteng, Kuya Tsikoy, Boknoy and many others.
electron geometry chart,Learn how to predict the shapes of molecules using Lewis electron dot structures and VSEPR theory. See the chart of electron-group geometry, molecular geometry, VSEPR notation and ideal bond angles for different numbers of electron groups and lone pairs. Tingnan ang higit paThis article explains the molecular geometry, which is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It covers how to determine the shapes of molecules using Lewis electron dot structures and valence-shell electron-pair . Tingnan ang higit pa
The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory states that electrons will spread themselves as far from each other as possible to . Tingnan ang higit paThe three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule is called molecular geometry. Understanding the molecular structure can help determine polarity, . Tingnan ang higit paTo determine the shapes of molecules we must become familiar with the Lewis electron dot structure which helps us identify . Tingnan ang higit paAfter calculating the electronic geometry from VESPR we can determine the molecular geometry based on the bonding orbitals. If there are no lone pairs .
Learning Objectives. To use the VSEPR model to predict molecular geometries. To predict whether a molecule has a dipole moment. The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to .Learn how to use VSEPR Theory to organize molecules based on their geometric structures. See examples of linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, octahedral, bent, trigonal pyramidal, seesaw, T-shaped, square .Learn how to use the VSEPR model to predict 3-D molecular geometry based on the number of valence shell electron pairs. Download free PDF and SVG charts of VSEPR shapes and bond .
Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3D! How does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs? Find out by adding single, double or triple .An electron group consists of a single, double, or triple bond. If lone pairs are present, the letter E n is added, where “n” represents the number of lone pairs surrounding the central atom. For .

Learn how to identify the molecular geometry and bond angles of a molecule using the VSEPR model. See examples of linear, trigonal, tetrahedral, and bent geometries and their corresponding bond angles.electron geometry chart VSEPR Theory & Chart Learn how to identify the molecular geometry and bond angles of a molecule using the VSEPR model. See examples of linear, trigonal, tetrahedral, and bent geometries and their corresponding bond angles.Explore the interactive simulation to understand how molecule shapes are determined by electron pairs and bond types.Learn how to predict the three-dimensional shape of a molecule using the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR). Find the AXE notation, bond angles, and examples for each molecular geometry type.
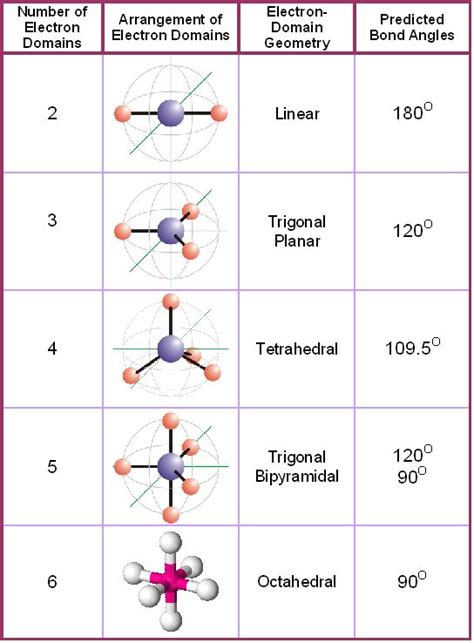
Electron-pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure. It is important to note that electron-pair geometry around a central atom is not the same thing as its molecular structure. The electron-pair geometries shown in Figure 7.16 describe all regions where electrons are located, bonds as well as lone pairs. Molecular structure describes the location of the atoms, not the electrons.Molecular Geometry Chart # of Electron Groups Number of Lone Pairs Electron Pair Arrangement Molecular Geometry Approximate Bond Angles 2 0 linear 180° 0 trigonal planar 120° 1 3 bent <20° 0 tetrahedral 109.5° 1 trigonal pyramid 4 <109.5° (~107°) 2 bent <109.5°(~105°) 0 trigonal bipyramidal 9 0°,12 1 see-saw <9 0°,<12
Explore our table of common electron geometries with bonding domains, bond angles, and formulas. Download PDF. Electron domains. Electron domain geometry. Bonding domains. . Molecular Geometry Chart; List of Acids & .Linear electron geometry: This ball-and-stick model represents a linear compound for formula . The two X atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. If the central atom also contains one or more pairs of non-bonding electrons, these additional regions of negative charge will behave much like those associated with the bonded atoms. The .Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3D! How does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs? Find out by adding single, double or triple bonds and lone pairs to the central atom. Then, compare the model to real molecules!
VSEPR Theory. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) is a theory that states that the 3d orientation, also known as the molecular geometry, of a molecule is not dependent on its chemical formula but on the repulsion of valence electrons.In other words, two molecules with the general formulas `AB_3` may look completely different in real life: one may be a pyramid .electron geometry chartValence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Lewis structures can determine properties such as geometry, bond orders, bond lengths, and dipoles for molecules. The Valence-Shell-Electron-Pair-Repulsion (VSEPR) theory can predict molecular geometry by minimizing electron-electron repulsion. It specifically uses the Coulombic repulsion between electrons as a basis for .What is a Molecular Geometry Chart? Molecular geometry is the science of representing molecules in a three-dimensional manner. A molecular geometry chart is a collection of rules on how molecules and electrons will connect and shape a molecule. Students and scientists can use these charts to create three-dimensional diagrams that represent .The electron-pair geometry provides a guide to the bond angles of between a terminal-central-terminal atom in a compound. The molecular geometry is the shape of the molecule. So when asked to describe the shape of a molecule we must respond with a molecular geometry. If asked for the electron-pair geometry on the central atom we must respond .
As such, this model of molecular geometry is often referred to as the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. For reasons that will become clear, extension of this model implies that a better name is the Electron Domain (ED) Theory. This model also accounts, at least approximately, for the bond angles of \(\ce{H_2O}\) and \(\ce{NH .Molecular Geometries from each Electron Domain Geometry Since electron pairs cannot be seen, the electron domain geometries are theoretical. The molecular geometries, also called shapes of molecules, are determined experimentally by X-ray diffraction. Even though the lone pairs cannot be seen, they still repel the bonding pairs of electrons.
An electron group consists of a single, double, or triple bond. If lone pairs are present, . Molecular Geometry Chart. The following table lists all the molecular geometries, the number of bond and lone pairs, and examples of each geometry type [5]. Number of Electron Pairs from Lewis Structure Key Terms: Electron Geometry, Lone Electron Pair, Molecular Geometry, VSEPR Theory. What is Electron Geometry. Electron geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering both bond electron pairs .
Electron Domain and Molecular Geometry Chart. VSEPR Theory, allows the 3-dimensional shape of most atoms to be determined. VSEPR Theory Geometries. Linear Molecule.

VALENCE-SHELL ELECTRON-PAIR REPULSION (VSEPR) MODEL Lewis structures show the two-dimensional distribution of atoms and electrons. The molecular geometry, or three-dimensional shape of a molecule or polyatomic ion, can be determined using valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (abbreviated VSEPR and pronounced “VES-per”) theory, in .VSEPR theory is a useful tool to understand the shapes and geometries of molecules based on the number and arrangement of atoms and electron pairs. In this webpage, you will learn how to apply the VSEPR theory to different types of molecules using the AXE notation and the VSEPR theory table. You will also see some examples of common molecular shapes and their bond .Electron-Pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure. It is important to note that electron-pair geometry around a central atom is not the same thing as its molecular structure. The electron-pair geometries shown in Figure 7.2.3 describe all regions where electrons are located, bonds as well as lone pairs. Molecular structure describes the location of the atoms, not the electrons.When the electron groups are all bond pairs, they are named exactly like the electron-group geometry. See the chart below for more information on how they are named depending on the number of lone pairs the molecule has. VSEPR Notation. As stated above, molecular geometry and electron-group geometry are the same when there are no lone pairs. .
electron geometry chart|VSEPR Theory & Chart
PH0 · Molecule Shapes
PH1 · VSEPR Theory: Explanation, Chart, and Examples
PH2 · VSEPR Theory: Explanation, Chart, and Examples
PH3 · VSEPR Theory & Chart
PH4 · VSEPR Chart
PH5 · Molecule Shapes
PH6 · Molecular Geometry: Definition, Chart, Shapes, and Examples
PH7 · Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles
PH8 · Geometry of Molecules
PH9 · 8.6: Molecular Geometries
PH10 · 10.2: VSEPR Theory